5.3 Turbulence models
The turbulenceProperties dictionary is read by any solver that includes turbulence modelling. Within that file is the simulationType keyword that controls the type of turbulence modelling to be used, either:
- laminar
- uses no turbulence models;
- RAS
- uses Reynolds-averaged stress (RAS) modelling;
- LES
- uses large-eddy simulation (LES) or detached-eddy simulation (DES) modelling.
If RAS is selected, the choice of RAS modelling is specified in a RAS subdictionary. The RAS turbulence model is selected by the RASModel entry from a long list of available models that are listed in Table A.5. Similarly, if LES is selected, the choice of LES modelling is specified in a LES subdictionary and the LES turbulence model is selected by the LESModel entry. Note that DES models are defined as a subset of the available LES models.
The entries required in the RAS subdictionary are listed in Table 5.3 and those for the LES subdictionary are listed in Table 5.4.
The incompressible and compressible RAS turbulence models, isochoric and anisochoric LES models and delta models are all named and described in Table A.5. Examples of their use can be found in the $FOAM_TUTORIALS.
5.3.1 Model coefficients
The coefficients for the RAS turbulence models are given default values in their respective source code. If the user wishes to override these default values, then they can do so by adding a sub-dictionary entry to the RAS dictionary, whose keyword name is that of the model with Coeffs appended, e.g. kEpsilonCoeffs for the kEpsilon model. If the printCoeffs switch is on an example of the relevant …Coeffs dictionary is printed to standard output when the model is created at the beginning of a run. The user can simply copy this into the RAS dictionary and edit the entries as required.
5.3.2 Wall functions
A range of wall function models is available in OpenFOAM that are applied as
boundary conditions on individual patches. This enables different wall function
models to be applied to different wall regions. The choice of wall function
model is specified through 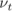 in the 0/nut file. For example, a 0/nut
file:
in the 0/nut file. For example, a 0/nut
file:
18dimensions [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0];
19
20internalField uniform 0;
21
22boundaryField
23{
24 movingWall
25 {
26 type nutkWallFunction;
27 value uniform 0;
28 }
29 fixedWalls
30 {
31 type nutkWallFunction;
32 value uniform 0;
33 }
34 frontAndBack
35 {
36 type empty;
37 }
38}
39
40
41// ************************************************************************* //
There are a number of wall function models available in the release, e.g. nutkWallFunction, nutUWallFunction, nutUSpaldingWallFunction. The user can consult the relevant directories for a full list of wall function models:
find $FOAM_SRC/TurbulenceModels -name wallFunctions
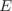 ,
,  and
and 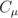 through optional E, kappa and Cmu keyword
entries.
through optional E, kappa and Cmu keyword
entries.
Having selected the particular wall functions on various patches in the nut/mut file, the user should select epsilonWallFunction on corresponding patches in the epsilon field and kqRwallFunction on corresponding patches in the turbulent fields k, q and R.
Further details on implementation and usage are available in the Extended Code Guide.


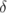 model
model