In the absence of sources and sinks, system behaviour is driven by its boundary conditions. These form a critical aspect of case specification where ill-posed combinations will lead to physically incorrect predictions, and in many cases, solver failure.
OpenFOAM offers a wide range of conditions, grouped according to:
Boundary conditions are assigned in the boundaryField section of the field files within each time directory for each mesh patch. The format follows:
boundaryField
{
<patch 1>
{
type <patch type>;
...
}
<patch 2>
{
type <patch type>;
...
}
...
<patch N>
{
type <patch type>;
...
}
}
Each condition is set in a dictionary given by the name of the underlying mesh patch, according to the type keyword.
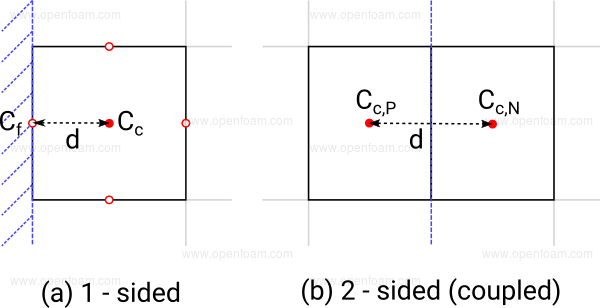
Used when solving the general transport equation to provide:
Usage
Function1 type to describe a property as a function of another, typically timeSource code:
See also:
| Would you like to suggest an improvement to this page? | Create an issue |
Copyright © 2016-2017 OpenCFD Ltd.